The ESP8266, developed by Espressif Systems, entered the market in August 2014 with the release of its first module, the ESP-01. This low-cost Wi-Fi system-on-chip (SoC) quickly gained traction in the Internet of Things (IoT) space due to its affordability and built-in connectivity, often priced under $5 for basic modules. It features a 32-bit Tensilica L106 RISC processor running at up to 160 MHz, with 64 KB of instruction RAM and 96 KB of data RAM for efficient task handling. The chip supports up to 16 MB of external flash memory for program storage and includes a full TCP/IP stack, enabling seamless Wi-Fi communication in station mode (connecting to existing networks) or soft access point mode (creating its own hotspot). Power consumption varies by mode: as low as 20 μA in deep sleep for battery-powered projects, up to 215 mA during transmission, and it operates on 3.3V with a wide temperature range of -40°C to 125°C for industrial use. Interfaces include 17 GPIO pins (multiplexed for UART, SPI, I2C, PWM, and ADC), an 10-bit analog-to-digital converter, and support for protocols like HTTP and MQTT, making it ideal for sensor networks, home automation, and remote monitoring.
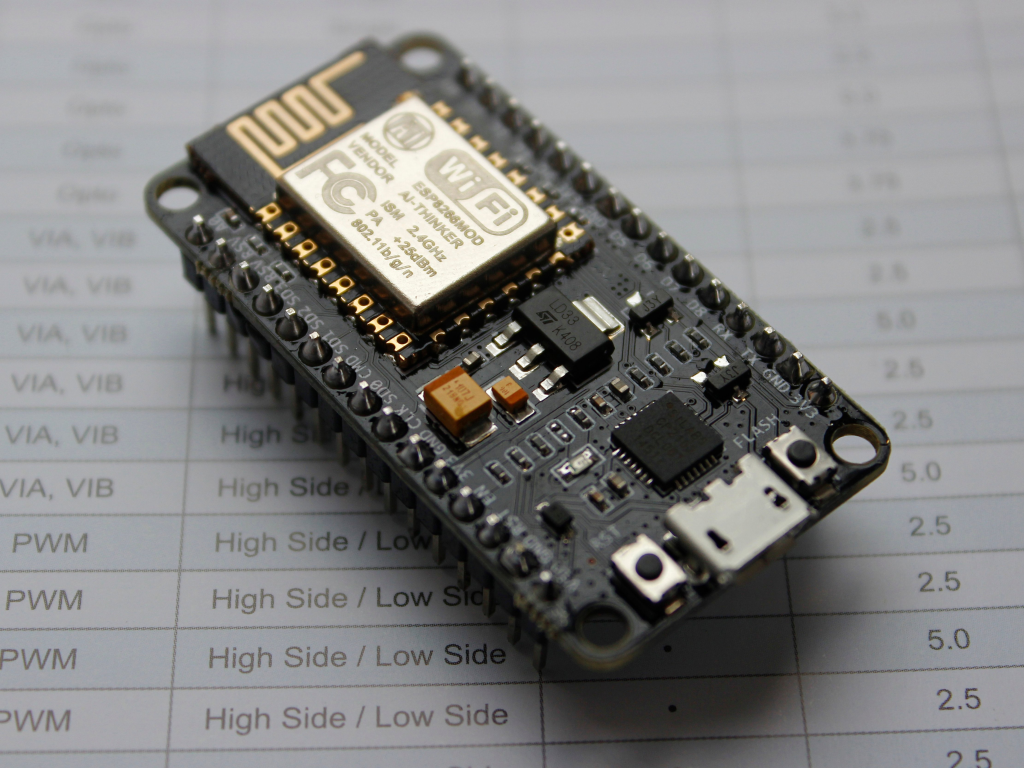
What sets the ESP8266 apart is its enduring popularity and market dominance. By 2023, Espressif’s Wi-Fi MCUs, led by the ESP8266, had secured the largest global market share for six consecutive years according to Techno Systems Research reports, contributing to over one billion total chip shipments worldwide. This success stems from its open-source ecosystem, including Arduino IDE compatibility and community-driven libraries, which lowered barriers for hobbyists and developers. Fun facts include its role in early IoT explosions—modules like the NodeMCU board simplified prototyping with built-in USB and regulators—and its influence on successors like the ESP32. Despite newer options, the ESP8266 remains a go-to for simple, reliable projects, powering everything from weather stations to smart door locks with minimal overhead.